Where is the New What
Spatiotemporal data describes where objects are and where they are moving. Prime examples are streams of IoT data from mobile devices, social platforms, static or moving sensors, satellites, wireless, and video feeds from drones and closed-circuit TVs. This data comes in the form of a reading, a timestamp (t), and location coordinates (x & y).
Why
Gartner reports the line between IoT-enabled sensors and location tracking is increasingly blurring as providers face increasing demand from clients to address location data along with other sensing information, such as asset status, direction of movement, temperature, and humidity.
These changes in time & space data are driving digital transformation in the areas of Automotive (e.g., connected car), Public Health (e.g., monitoring spread of disease) and Safety (e.g., threat hunting), Security (e.g., common operational picture), Logistics (e.g., fleet monitoring), Environment and Climate (change detection), Retail (e.g., proximity marketing), and many others.
How
Existing databases (even with special object-relational extensions for spatio-temporal data) have struggled to keep up the scale, speed, and specialized analytics required for modern location intelligence workloads. They were never designed to handle the variety of fusion steps and aggregations in an acceptable latency profile required to power downstream value-added location aware services.
A new paradigm, commonly referred to as vectorized databases, are radically reducing the complexity and increasing the performance of spatiotemporal workloads. Vectorization is extremely efficient at calculating changing geometry over time.
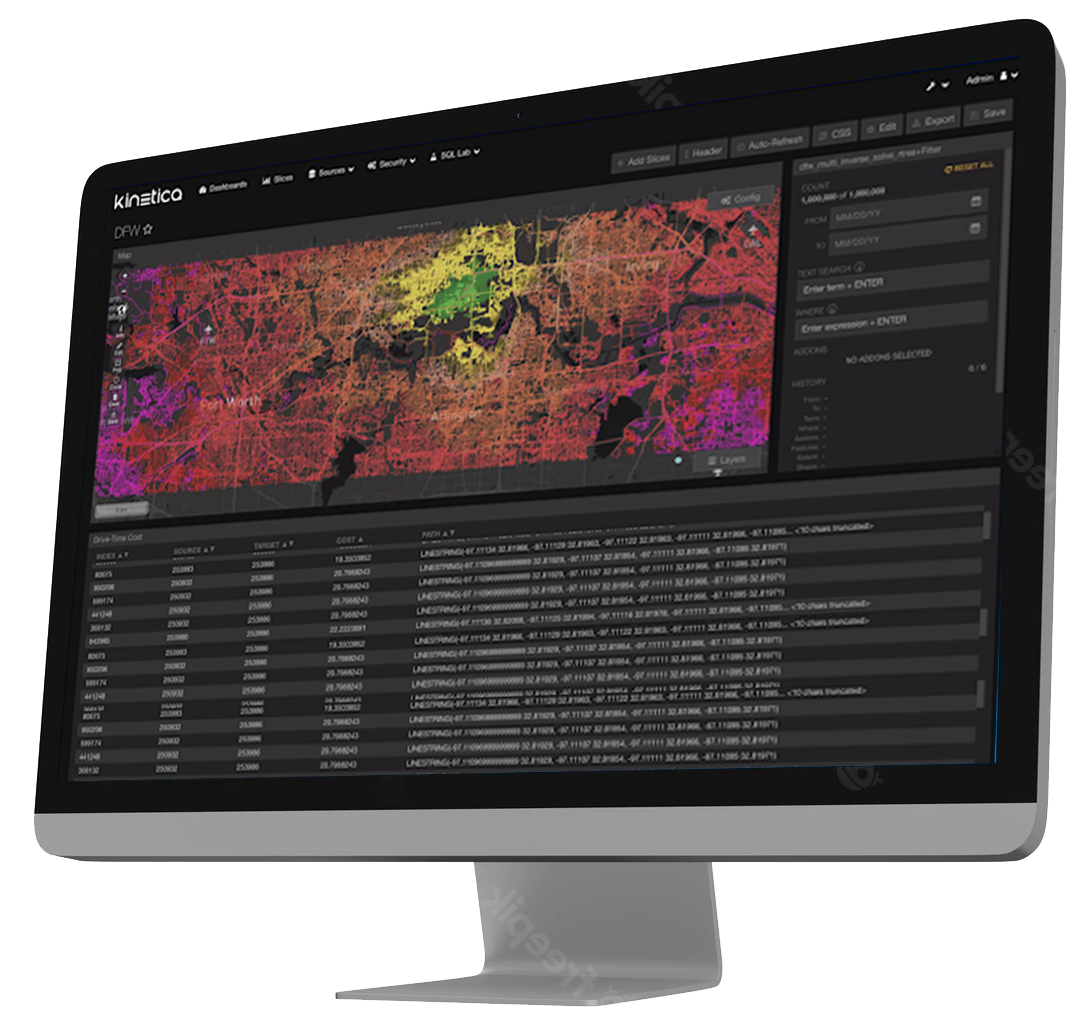
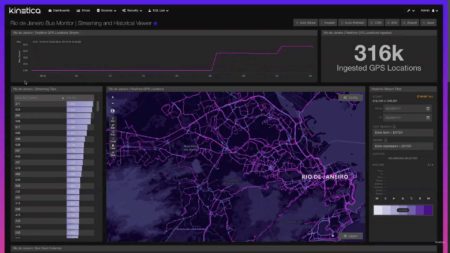
Kinetica enables interactive exploration of massive quantities of streaming data.
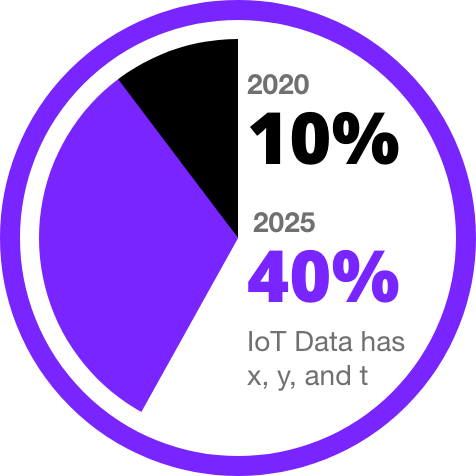
Data is Changing
Real-time geospatial data is proliferating as prices continue to fall dramatically on the technology that generates this data.
| Then | Now | |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Static, authoritative data | Streaming, noisy data |
| Sources | Surveys (e.g., census, polls, etc.), satellites, and transactions | Sensors, smartphones, telemetry, drones, closed-circuit TVs, satellite constellations, bluetooth tags |
| Volumes | Megabytes to gigabytes | Terabytes to petabytes |
| Velocity |
|
|
Uses are Changing
New and innovative uses of real-time data were first pioneered by leading tech companies such as Uber and Tesla. But those demands are being felt by many other companies and industries.
| Then | Now | |
|---|---|---|
| Persona | GIS Specialists | Developers, Architects, Analysts, GIS Specialists |
| Use Cases |
|
|
| Questions |
|
|
| Exemplary examples |
Starbucks, Walgreens, Gallup Poll, Municipalities | Uber, Ford, Apple, Verizon, Tesla, U.S. Air Force, Amazon, Liberty Mutual, British Petroleum |
Tools are Changing
Modern real-time geospatial analytics tools are designed to make it easy to work with the volume, speed and noise of moving data.
| Then | Now | |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Client-Server | Cloud |
| Tools |
|
|
Modernize IoT Data Management & Analytics
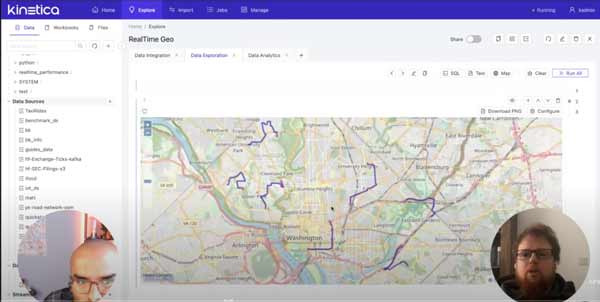
Nima Negahban, CEO of Kinetica, demonstrates how Kinetica helps streamline and simplify data management when working with IoT data and analytics.
Making Sense of Sensor Data
As sensor data grows more complex, legacy data infrastructure struggles to keep pace. A new set of design patterns to unlock maximum value. Get this complimentary report from MIT Technology Review:

Kinetica: For the Next-Generation of Geospatial Applications
What Can You Build with Kinetica?
Smart Cities Advanced Monitoring
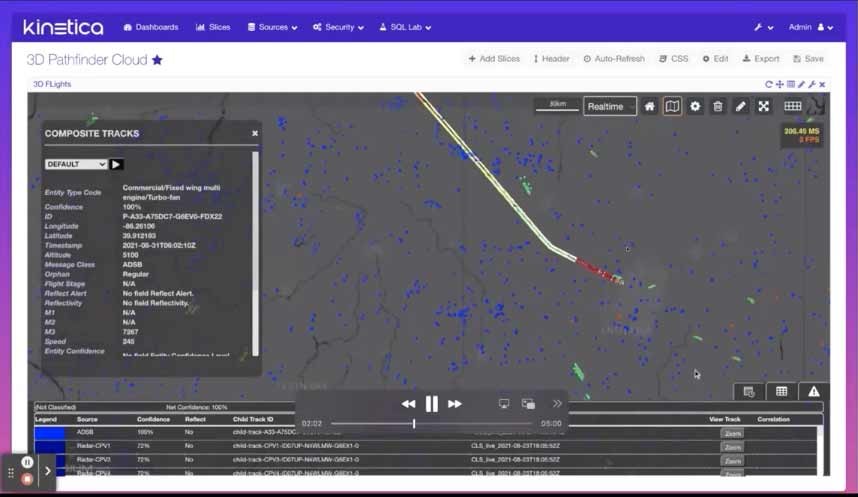
Track Entities in Real-time
Connect Multiple Feeds through Time with ASOF Joins
Book a Demo!
The best way to appreciate the possibilities that Kinetica brings to high-performance real-time analytics is to see it in action.
Contact us, and we'll give you a tour of Kinetica. We can also help you get started using it with your own data, your own schemas and your own queries.