Kinetica vs PostGIS
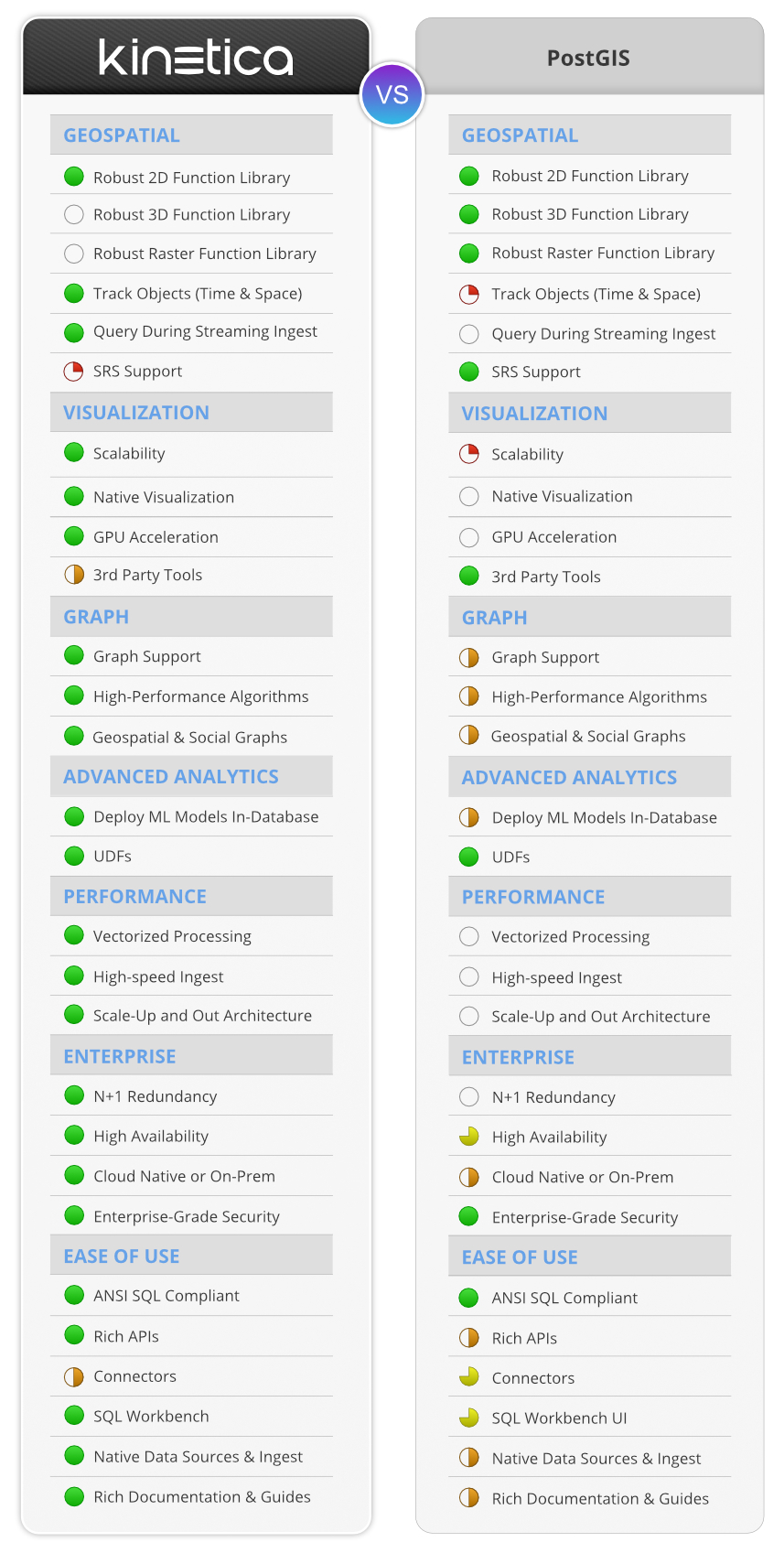
PostGIS is a capable open-source geospatial extension for PostgreSQL. Kinetica is a modern purpose-built database for geospatial analytics at scale and speed.
What is Kinetica?
Kinetica is a high performance real-time database designed from the ground-up for analysis of geospatial data at speed and scale.
Kinetica scales horizontally with a memory-first distributed architecture which allows you to handle larger geospatial data sets with ease. An eventually-consistent, no-locking design allows for simultaneous ingest and analysis with no latency.
What is PostGIS?
PostGIS is an extension for the open-source PostgreSQL database that provides geospatial data types, functions, and queries. First released in 2001, PostGIS has provided a functional way for users to build custom geospatial applications, without needing to pay for licenses from GIS vendors such as ESRI.
What is Kinetica good for?
Kinetica is designed for time-series and spatial analytics (OLAP) workloads, and stands out when used with large volumes IoT data, such as that from moving sensors, where there are frequent updates of location.
Gaining value from such data requires advanced capabilities to blend spatial, time series, and graph analytics. Kinetica has over 100 spatial functions including geo-joins, point in polygon, and map matching, and can create interactive visualizations with billions of geospatial data points. Kinetica combines this with advanced time series functions and also allows you to seamlessly use relational data in a native graph context for understanding relationships.
Kinetica’s vectorized query algorithms are blazing fast and allow you to do analysis that you wouldn’t have thought possible. It’s distributed architecture allows you to do geospatial analysis at scale never before possible.
What is PostGIS good for?
PostGIS has become very popular among GIS developers. Its open source license makes it low cost to get started with, and it has a strong community of users, so finding expertise to develop or administer it is quite easy. PostGIS provides a very robust geospatial function library of both 2D, 3D, and raster functions. It has full support for many spatial reference systems (SRS), and plugs into popular 3rd party tools to provide missing functionality, such as for visualizations or routing algorithms.
PostGIS makes it easy for organizations to build geospatial applications at a moderate scale.
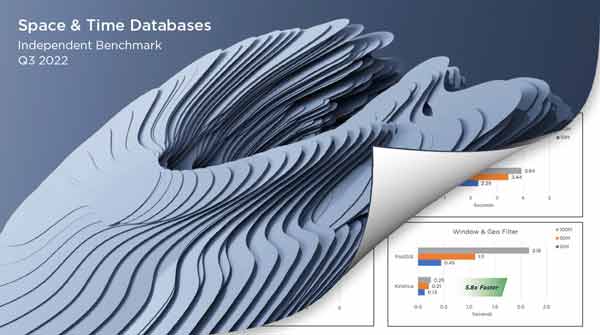
Kinetica outperformed PostGIS in every query and was the only database to pass all feasibility tests across geospatial, time-series, graph, and streaming.
Spatial & Time Series Database Study
Topics covered include:
- Business questions and scenarios that require spatial and time-series data as the basis for the benchmark study
- Database SQL feasibility for analyzing geospatial and temporal data
- Working with relational and native graph databases, streaming data, and in-database visualizations
- Performance results and factors that impact business analysis
Try Kinetica Now:
Kinetica Cloud is free for projects up to 10GB
What are PostGIS' limitations?
Users often run into limitations with PostGIS when working with geospatial data at a large scale. PostGIS is not set up with a memory-first, scale-out architecture, and it does not support vectorized processing that taps into GPUs and vectorized CPUs, so its performance is capped when data volumes grow very large.
As a result, PostGIS also cannot provide a level of visual interactivity with large and detailed geospatial datasets. Its queries take too long to return results, and without native support for visualization, it may face additional scale limitations from the 3rd party visualization tool it is plugged into. Many popular visualization vendors leverage client-side rendering, which limits visualizations to small and manageable datasets.
Postgres is not designed for high velocity data ingestion, with real time aggregations and queries, so PostGIS will only allow users to gain insights from their geospatial data after the fact.
When should you use Kinetica?
Kinetica is the choice for users who are running up against the scale limitations of PostGIS. Kinetica is a horizontally scaling distributed system with a memory first architecture, built natively for vectorization to take full advantage of GPUs and vectorized CPUs. This allows Kinetica to scale to handle far larger geospatial data sets, and provide much faster analytics on equivalently sized systems to PostGIS.
Kinetica leverages WMS server-side rendering to enable interactivity with massive, detailed geospatial datasets. This grants users an interactive data exploration experience at a virtually unlimited scale, all natively within Kinetica.
Kinetica is also the pick for users who require support for streaming, graph, or machine learning capabilities in their use case. Kinetica provides simultaneous streaming data ingest and analysis, all in the context of historical and integrated data. Additionally, Kinetica incorporates robust graph analytics capabilities, as well as the ability to obtain machine learning inferences against geospatial data.
Scale past PostGIS with Kinetica
Spatio-temporal data requires new capabilities to join, analyze, and visualize in order to extract value.
Low Latency Joins
Context matters. Sensor data must often be combined with historical, integrated data without sacrificing data freshness. Kinetica makes it quick and fast to join high-cardinality data on inexact keys.
Time-Series & Spatial Functions
Tried and tested functions for working with times and datws and over 130 OGC high-performance geospatial functions are available with SQL or using the REST API. Functions include tools to filter, compare or aggregate data by area, by track, or custom shape.
Spatial Funtions »
Server Side Visualizations
Exporting large volumes of data to the front-end for rendering is expensive and slow. Kinetica generates server-side visualizations that can be sent to the front end as WMS tiles.
Window Functions »
Case Study: Kinetica in Telecoms
It needed to blend mobile network performance data with 90B phone signal events, all overlaid on road network data, to understand its performance in key geographic areas, and determine how to prioritize infrastructure improvements.
The massive scale geospatial operation required, joining billions with billions of rows, would have required 6 years to complete on PostGIS — a nonstarter. Kinetica was able to return the workload in 50 minutes. This is a prime example of the type of complex, large scale geospatial analysis that is a better fit for Kinetica.